Implantation
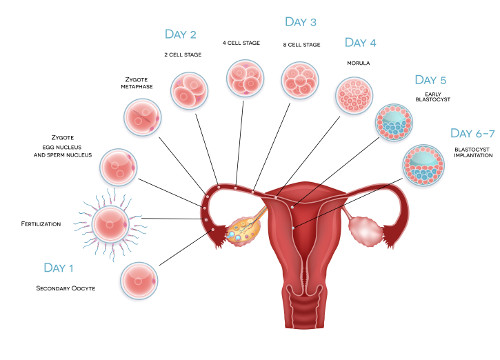
What is implantation?
The fertilized egg has divided and become a blastocyst, and has traveled from the fallopian tube to the uterus. Once in the uterus the blastocyst will burrow into the lining of the uterus in order to receive receive oxygen and nutrients from the mother, this process is called implantation. Only 50-80% of fertilized eggs successfully implant in the womb. Once implanted, the part of the embryo that will become the placenta begins to produce the hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The hormone hCG is present in a woman's blood and urine, and is detected by home pregnancy tests and blood tests performed by your doctor or lab.
Signs of implantation
While many women do not experience any symptoms at the time of implantation you may notice one or more of the following:
- Cramping - Some women notice mild to moderate cramping at the time of implantation as the uterus contracts and shifts during the process
- Implantation bleeding - Some women report light spot spotting 7-10 days after ovulation, this is known as implantation bleeding and is dark in colour (not bright red) and does not last long (it is caused by the disruption of the uterine lining as the embryo burrows in)
- Basal body temperature shift - If you chart your basal body temperature, you may notice a slight (a few tenth's of a degree) increase or decrease in temperature at the time of implantation
Once implantation has occurred, changes begin to occur physically and hormonally and some women will begin to experience the early symptoms of pregnancy.


